Why Ki-67?
Although it is an important biomarker in oncology (mostly in breast and prostate), Ki-67 immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis has yet to be standardized. Working groups have provided guidelines for Ki-67 scoring in different cancer types to limit pathologist’s variability.¹,²
Rapid and robust AI solutions to assist scoring have recently emerged in evaluating Ki-67. In this study, the results of Ki-67 scoring performed with the Aiforia® Platform (deep learning AI platform) were compared against three independent pathologists on various solid tumors.
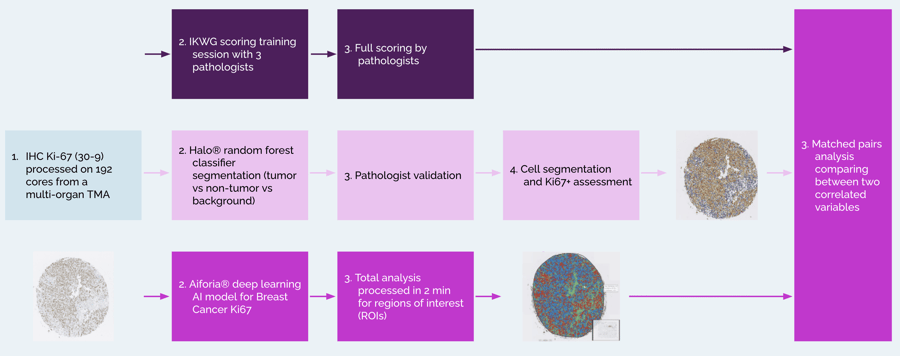
The workflow
Cerba Research stained 192 tumors of various origins, including breast and prostate, with the CONFIRM anti-Ki-67 clone (30-9) (ROCHE monoclonal primary antibody (IVD)) on the Ventana Benchmark Ultra. Three pathologists were appropriately trained following the International Ki-67 Working Group (IKWG) recommendations and scored tissues accordingly.³
Key takeaway
Out of 192 cores, only 158 were analyzed due to the absence of tissue and/or pathologists' inability to score. Depending on the analysis approach applied, Ki-67+ cells were detected in 24.38 - 28.71% of the tumor cells. The study shows a very high consistency of results obtained for Ki-67 scoring between the two image analysis software (r2=0.95) on solid tumors analyzed (n=158). However, the correlation obtained between the pathologists was weaker (mean r2=0.83), despite appropriate training and following guidelines, but remains within an acceptable range.
AI data quality and speed of execution
Rania Gaspo, Global Therapy Area Lead from Cerba Research, comments on the results: “In a nutshell, this work shows that recent AI-based image analysis tools, such as the Aiforia® Platform, provide valuable assistance in the field of image analysis and allowed us to drastically reduce inter-pathologist variability in the Ki-67 scoring of solid tumors. We were also positively surprised with the speed of execution of the Aiforia® Platform, which was able to process regions of interest for all cores in just 2 minutes, saving us a lot of time and effort.”
Read more on the ESMO 2023 poster: “Pichon X, Gaspo R, Iglesias S, Kumar D, Tliba M, Burrer R, Finan A. Evidence for the utility of artificial intelligence (AI) and image analysis in Ki-67 quantification in solid tumors. Presented at: ESMO annual meeting; October 20-24, 2023; Madrid, Spain”.
References
1. Polley, M. et al. (2015, June). An international study to increase concordance in Ki-67 scoring. Mod Pathol., 28(6), 778-786. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2015.38
2. Nielsen, T. et al. (2021, July 1). Assessment of Ki-67 in Breast Cancer: Updated Recommendations From the International Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. J Natl Cancer Inst., 113(7), 808-819. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djaa201
3. Welcome to Ki-67-QC calibrator. URL http://www.gpec.ubc.ca:8080/tmadb-0.1/calibrator/index