What is veterinary pathology?
Veterinary pathology is a multifaceted field within veterinary medicine that focuses on diagnosing diseases in animals. This discipline is foundational for maintaining animal health and, by extension, human health. Veterinary pathology encompasses diagnostic, research, and preclinical facets, each serving a critical role in understanding and managing animal diseases:
- Diagnostic veterinary pathology involves the examination of tissues, body fluids, and organs to diagnose diseases in animals. Veterinary pathologists play a crucial role in identifying and characterizing diseases, aiding in treatment decisions and disease management.
- Research veterinary pathology focuses on investigating the mechanisms, causes, and treatments of diseases in animals. This branch contributes to advancing veterinary medicine, developing new therapies, and understanding disease processes.
- Preclinical veterinary pathology focuses on assessing the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and other interventions in animals before they are applied clinically. This branch plays a critical role in drug development, ensuring the safety of treatments and minimizing risks to animal and human health.
How does artificial intelligence fit into the picture of veterinary pathology?
AI is increasingly being integrated into veterinary pathology, revolutionizing the way pathologists diagnose diseases and conduct research. AI applications in veterinary pathology include:
- Image analysis: AI analyzes images, aiding pathologists in identifying abnormalities and diagnosing diseases, including tumor detection, cell classification, and quantification of features.
- Pattern recognition: AI recognizes patterns, aiding pathologists in identifying disease trends, correlations, and biomarkers, particularly useful for research uncovering disease mechanisms.
- Diagnostic assistance: AI systems can serve as diagnostic aids, providing pathologists with second opinions and assisting in decision-making.
- Predictive modeling: AI can help predict disease using patient history, lab results, and imaging, helping pathologists anticipate progression and tailor treatments for better outcomes.
AI can solve challenges in veterinary pathology
Veterinary pathologists often encounter complex diseases with diverse presentations and overlapping symptoms. AI can assist in disease diagnosis by analyzing digital images of tissues and body fluids, identifying subtle patterns and abnormalities that may not be apparent to the human eye.
Pathologists may interpret histopathological images differently due to variations in experience, training, and subjective judgment. AI can help reduce interpretation variability by standardizing analysis methods and criteria.
Diagnostic laboratories often face high caseloads with tight turnaround times, which can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment. AI-powered image analysis tools are likely to become more useful in automating routine tasks, such as image and scanning quality control, sample triage, image annotation, and preliminary diagnosis, allowing pathologists to focus their time and expertise on challenging cases. This can help reduce workload and improve turnaround times.
AI also has the ability to reduce fatigue by reducing the need for laborious or repetitive tasking such as counting (for example mitotic figures or cell counts), measuring (such as nuclear or cell diameters), or searching for fine details (i.e., binucleated or multinucleated cells amongst neoplastic mononuclear cell populations). The use of assistive AI means the results produced are used to support the pathologist in making decisions.
AI-based telepathology systems can overcome geographical barriers by enabling remote consultation and diagnosis. Pathologists can use digital imaging and AI algorithms to analyze samples from distant locations, expanding access to veterinary pathology services and improving patient care.
To summarize, AI offers five crucial benefits to veterinary pathologists:
- Enhanced accuracy: AI algorithms can analyze large volumes of data with high precision, leading to more accurate diagnoses and prognoses.
- Time savings: AI automates repetitive tasks, allowing pathologists to process samples and interpret results more quickly.
- Improved productivity: With AI handling routine tasks, veterinary pathologists can devote more time to complex cases, research endeavors, and professional development.
- Consistency: AI ensures consistency in diagnostic interpretation by standardizing analysis methods and criteria. This consistency is particularly valuable in multicenter studies and longitudinal research projects, where uniformity is essential for accurate comparisons and conclusions.
- Expanded knowledge base: AI facilitates the aggregation and analysis of vast amounts of data from diverse sources, leading to the discovery of new disease markers, therapeutic targets, and treatment strategies.
Examples of real-world AI applications
The absolute and relative area of high-quality tissue in HE and IHC images serves as a triage to flag quality issues in scanning and wet-lab procedures before the material even reaches the pathologists, saving time and monitoring quality issues within the laboratory workflow. AI can help detect artifacts such as folded tissue, mounting artifacts, air bubbles, pen markings, dust, foreign material fibers, and poor-quality tissues.
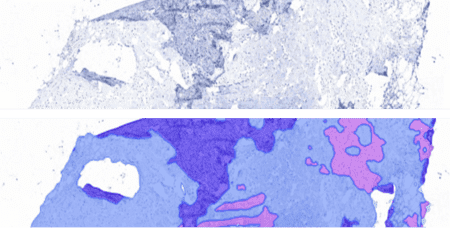
Organ detection AI enables cross-checking of image content against metadata / LIMS information and enables automated mapping of images for further analysis with additional, organ or lesion-specific AI models. This can increase workflow efficiency, especially with a quality control application (image and scanning quality control). The application is especially useful in large toxicopathology studies which can include more than two thousand images.

AI-powered image analysis is used in cellular neuroscience to analyze sample tissues on microscopic slides. The technology is utilized to quantify brain areas and count specific cell types within them. The AI model can calculate thousands of cells in less than a minute. Finally, distance calculations between cells and area borders can be extracted from the images with the help of analytical tools.
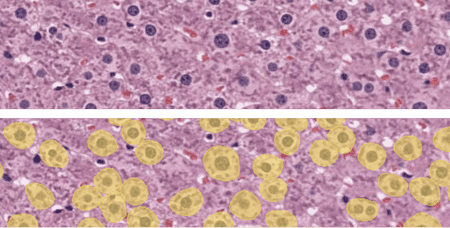
Liver tissue hypertrophy, characterized by an increase in cell size, is a critical pathological feature observed in various liver diseases. Accurate measurement of cell hypertrophy is essential for understanding disease progression and assessing therapeutic interventions. However, manual measurement methods are time-consuming and subjective. Using AI, hepatocyte hypertrophy can be detected in hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) stained liver samples. The exact sizes of the cells and their spatial metrics can also be reported for cell hypertrophy studies.
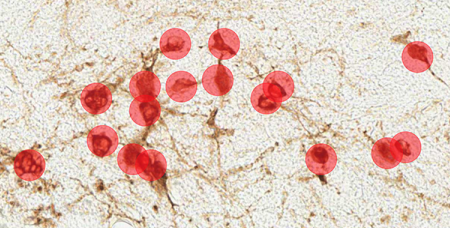
Immunohistochemical staining of canine mast cell tumors for the proliferation marker Ki67 (Ki67-index) is used to predict the survival in cutaneous mast cell tumor canines. Even though the approach is a good diagnostics tool, counting the positive cells is time-consuming. However, reliable results can be achieved with automated image analysis, as the AI-powered tools do the job in just a few seconds, giving veterinary pathologists a needed leverage to their diagnostic work. Aiforia’s team has been working closely with Finn Pathologists to develop this commercial model.
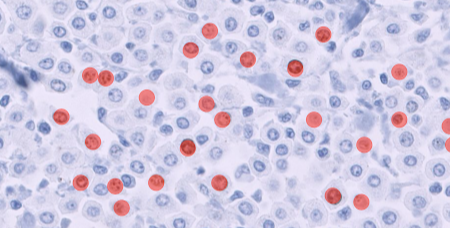
Bone marrow is a vital tissue for analysis in pharmacologic safety studies. The cellularity assessment traditionally consists of cell counts and applied mathematical modeling, a time-consuming and non-practical task at scale. AI models can be trained to differentiate hematopoietic cells from the tissue. This automates cell counting and provides an objective and replicable measure of bone marrow cellularity. Read more about Veterinary Pathologist Mark Smith's work on AI-assisted screening of bone marrow cellularity changes.
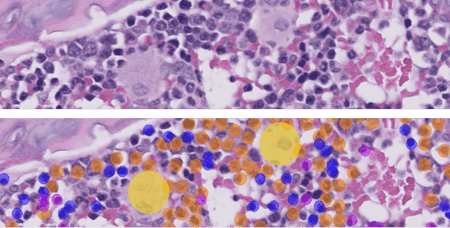
Technological advancements are helping pathologists reach more accuracy with less effort. AI-powered image analysis is gaining popularity among experts and gaining a place in veterinary medicine as a standard, under-the-belt tool. As more work segments are automated, further resources can be used for critical tasks requiring higher problem-solving skills and creativity.
Learn more about the use of AI in veterinary pathology by diving into our case studies: